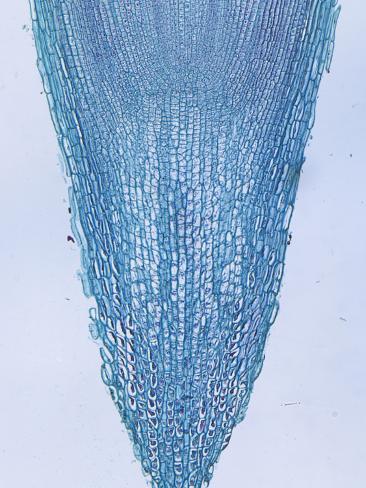
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. However, roots can also be aerialor aerating (growing up above the ground or especially above water). Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either (see rhizome).Therefore, the root is best defined as the non-leaf, non-nodes bearing parts of the plant's body. However, important internal structural differences between stems and roots exist.
Parts of a Root
 Root Hairs
Root Hairs The root hairs are thin, hairlike outgrowths of a root.
The root hairs absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Root Caps
The root caps are groups of tiny cells
which grow at the tips of roots.
Root caps are spherical in shape.
The root caps help to protect the root
tip from the roughness of the soil as
roots grow in search of water.
Primary Root
the root. The primary root is usually
located directly below the main stem
of the plant. The primary root is the
main path from the smaller roots to
the stem. Sometimes the primary
root stores food for the plant.
Secondary Root
The secondary roots are roots which
branch off from the primary root.
Secondary roots grow down at an angle.
Secondary roots serve as a pathway
for food and water from the root
hairs to the primary root.


No comments:
Post a Comment